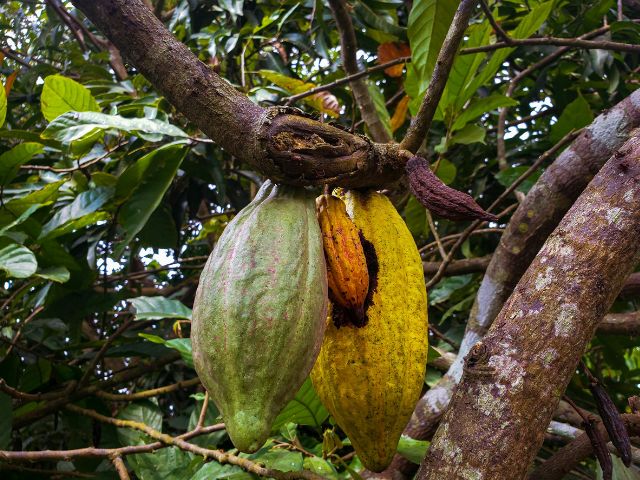
A close-up of cacao pods hanging from a tree branch. One pod is green and healthy, while the other is yellowed. The tree’s bark is rough, surrounded by green leaves. Credit: Tope A. Asokere on Pexels.
The Chocolate Crisis You Didn’t See Coming
Imagine walking into your favorite store, craving a bar of smooth, rich chocolate, only to find that prices have skyrocketed—or worse, your favorite brand is no longer available. It sounds extreme, but this could be the reality in the not-so-distant future. West Africa produces 70% of the world’s cacao, the key ingredient in chocolate, but climate change is making it harder to grow. Rising temperatures, unpredictable rainfall, and increasing crop diseases are threatening cacao farms.
This isn’t just bad news for chocolate lovers. Millions of farmers depend on cacao to feed their families and support their communities. If cacao production continues to decline, their livelihoods—and the world’s chocolate supply—are at risk.
Where Does Chocolate Come From? (And Why Should You Care?)
Most of us don’t think about where chocolate comes from—we just enjoy it. But before that delicious bar reaches your hands, it starts as a pod growing on a delicate cacao tree.
Cacao trees thrive in warm, humid climates, but there’s a catch—they can’t handle extreme heat. The ideal temperature for cacao trees is below 32°C (89.6°F), and anything hotter can start causing serious problems.
The biggest producers of cacao—Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Cameroon, and Nigeria—rely on these trees for their economies. More than 9 million farmers and workers depend on cacao farming to survive. But now, climate change is pushing temperatures past safe levels, and cacao trees are suffering.
Rising Temperatures Are Hurting Cacao Farms
Cacao trees have been growing in West Africa for centuries, but in recent years, farmers have noticed something disturbing: it’s getting too hot for their crops.
- Since 2015, Ghana and Côte d’Ivoire have had 40 extra days per year where temperatures rise above 32°C.
- In 2024, 71% of cacao-producing areas experienced six extra weeks of extreme heat.
Why does this matter? Because excessive heat weakens cacao trees.
- Too much heat reduces photosynthesis, slowing growth and lowering cacao yields.
- Cacao pods shrivel up or grow smaller, reducing the amount of chocolate that can be made.
- Farmers are losing money, and global chocolate prices are rising.
One farmer in Côte d’Ivoire described it best:
The leaves used to protect our cacao pods from the sun. Now, they fall off too soon, and the pods dry out before we can harvest them.
The result? Lower quality cacao, smaller harvests, and more expensive chocolate.
Too Much Rain, Then Not Enough
If rising temperatures weren’t bad enough, cacao trees now face another major problem: wildly unpredictable rainfall.
Cacao farming depends on steady, well-distributed rain—about 1,500 to 2,000 mm per year. But thanks to climate change, rainfall has become chaotic:
- In July 2024, Côte d’Ivoire received 40% more rain than expected. Farms flooded, cacao pods rotted, and entire crops were lost.
- In December 2024, some regions received almost no rain. Without water, cacao trees wilted, and pods stopped growing.
It’s a double disaster: too much rain drowns the crops, too little leaves them starving. Farmers can’t predict when to plant or harvest, and each year gets more uncertain.
It’s Not Just the Weather, There are Other Threats to Cacao Farming
As if extreme heat and unpredictable rainfall weren’t enough, cacao farmers face even more obstacles.
Pests & Diseases Are Spreading Faster Than Ever
Warmer temperatures help pests thrive, especially mealybugs, tiny insects that spread the deadly Cacao Swollen Shoot Virus (CSSV).
- 600,000 hectares of cacao farms in Ghana were infected with CSSV in 2023.
- This disease alone caused a 17% drop in Ghana’s cacao production.
When cacao trees get infected, they stop producing pods and eventually die. Farmers are losing entire farms to this disease, and finding ways to stop it is difficult.
Smuggling & Illegal Mining are Stealing Cacao Farmers’ Livelihoods
Cacao farming is already tough work, but low wages are forcing some farmers to sell their crops to smugglers or even give up farming entirely.
- Ghana lost 160,000 tons of cacao to smugglers in the 2023/2024 season—three times more than the previous year.
- Some farmers are leasing their land to illegal miners because mining pays better than farming.
The problem? Mining damages the land, making it impossible to farm cacao again. Once a farmer gives up their land, they may never be able to return to growing cacao.
Can Anything Be Done? Yes—But It Will Take Effort.
Despite these challenges, there are solutions that can help protect cacao farming. Here’s what’s being done:
Planting Shade Trees (Agroforestry)
- Farmers are planting taller trees, like banana, mango, and cashew, to protect cacao from extreme heat.
- These trees cool down cacao farms and improve soil moisture.
Fighting Pests & Disease
- Scientists are working on disease-resistant cacao trees to fight CSSV.
- Better pest management techniques could reduce losses by 17% per year.
Fair Trade & Financial Support
- Programs that pay farmers fair wages reduce smuggling and illegal mining.
- More financial support means farmers can afford climate adaptation strategies.
These solutions are helping, but they need global support to make a real impact.
You might be wondering—what can I actually do? Here are some ideas:
- Choose ethical chocolate by looking for Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, or Direct Trade labels. These brands support sustainable cacao farming and fair wages for farmers.
- Support reforestation projects. Some groups help plant shade trees on cacao farms to protect crops from climate change. Supporting these efforts helps cacao trees survive extreme weather.
- Tell your friends and family about this issue.
Final Thoughts
Chocolate isn’t just a treat—it’s a lifeline for millions of farmers. But if climate change continues at this rate, chocolate could become a rare luxury. The good news? We still have time to act. By choosing sustainable chocolate, supporting reforestation, and spreading awareness, we can help protect cacao farming for generations to come.
Source: Climate Central. (2025, February 12). Climate change is heating up West Africa’s cocoa belt. Climate Central. Retrieved from https://www.climatecentral.org/