Artwork for Bill Madden’s music video “Mother”. The artwork was created by Kasia Haldas. CC BY-NC-ND 3.0.
Introduction
African elephants, the majestic giants of the savannah and forests, are facing unprecedented threats from habitat loss, human-wildlife conflicts, and the looming specter of climate change. A recent study by Simon Nampindo and Timothy O. Randhir, published on January 31, 2024, in PLOS Sustainability & Transformation, uses dynamic modeling to unravel how these factors are influencing elephant populations in the Greater Virunga Landscape (GVL), a biodiversity hotspot in Africa.
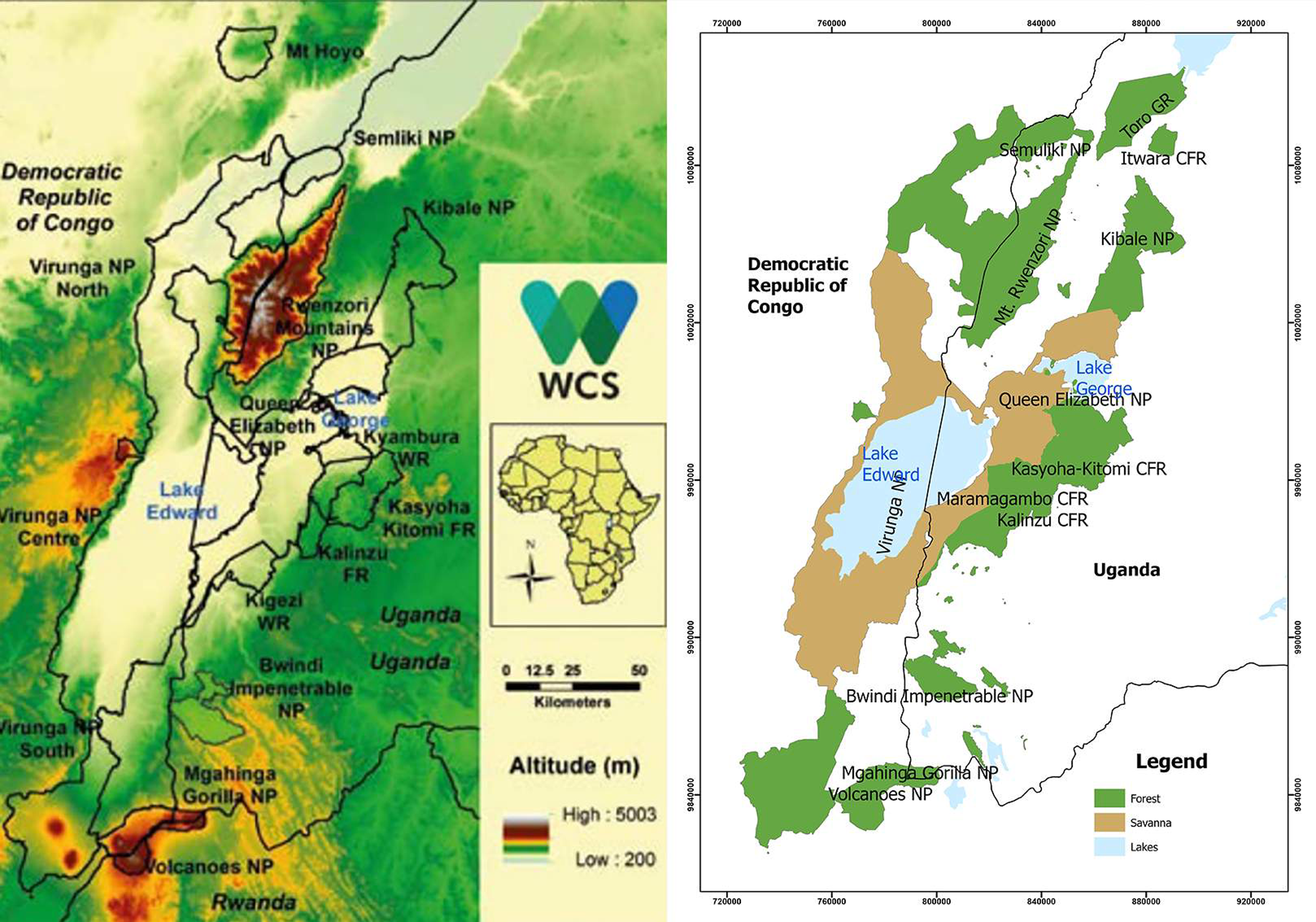
Greater Virunga Landscape (GVL) with vegetation map. Developed by Simon Nampindo and Timothy O. Randhir in collaboration with the WCS Uganda program. The GVL straddles Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Understanding the African Elephant Crisis
The African elephant, once roaming freely across vast stretches of the continent, is now confined to fragmented habitats, with populations experiencing alarming declines. The 2016 IUCN African Elephant Status Report highlighted a 30% decline over ten years, with human activities and climate change at the heart of this crisis. Elephants play a pivotal role in their ecosystems, from seed dispersal to landscape modification, making their decline a matter of global environmental concern.
The Study: A Closer Look
Nampindo and Randhir’s study is a testament to innovative conservation science, employing dynamic simulation models to analyze the effects of changing climates, habitat loss, and water resource availability on the age-class structure of elephant populations. Their research, underpinned by data from the GVL — an area spanning Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo — provides a comprehensive understanding of how different age classes of elephants respond to environmental stressors. This approach is crucial for developing targeted conservation strategies.
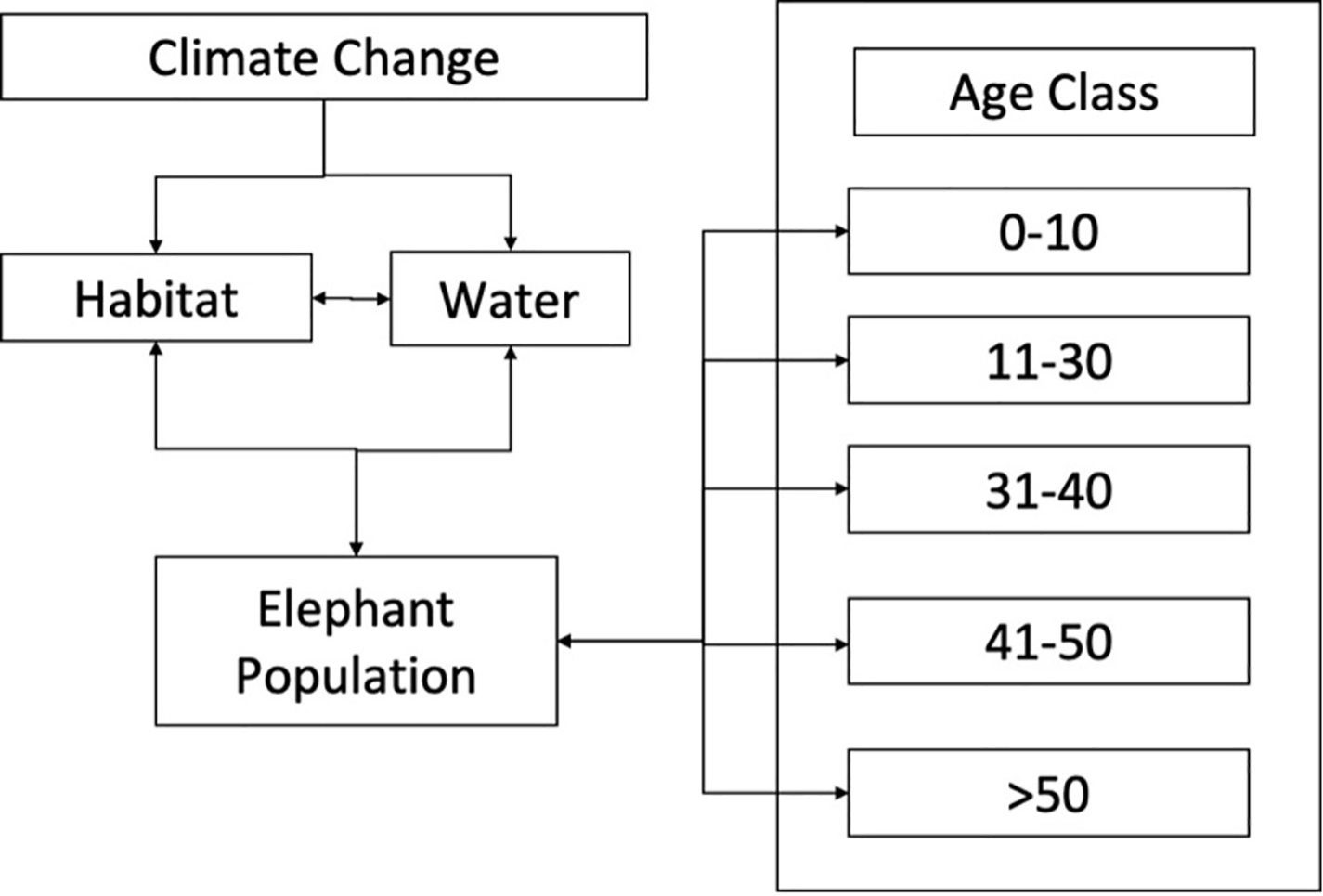
Conceptual model for population dynamics of elephants in GVL, linking climate, habitat changes, and resource variability to population shifts over 50 years.
Key Findings
The study reveals several critical insights:
- Climate Change Impacts: Older elephants are more vulnerable to climate change, affecting their survivability and migration patterns. This vulnerability is attributed to direct impacts, such as disease and physiological stress, and indirect ones, like habitat alteration and drought-induced deaths such as fire and risk of predation.
- Habitat and Water Resources: An improvement in habitat quality and water availability positively affects elephant populations, emphasizing the need for conservation efforts that enhance these critical resources.
- Future Projections: Without mitigating environmental and anthropogenic stressors, the GVL could see a demographic shift towards younger elephants, potentially impacting the long-term viability of these populations.
Conservation Implications
The research underscores the necessity for a transboundary management approach, incorporating climate change mitigation, cooperation among conservation agencies, and partnerships with relevant stakeholders. It also highlights the importance of understanding age-specific responses of elephants to environmental changes, facilitating the development of comprehensive conservation strategies that address water availability and habitat quality.
To ensure the survival of African elephants in the face of climate change and habitat loss, the study recommends:
- Enhanced Transboundary Cooperation: Strengthening collaboration across borders to ensure cohesive conservation efforts.
- Habitat Restoration and Protection: Implementing measures to improve habitat quality and connectivity, including reforestation and the establishment of wildlife corridors.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts, providing them with sustainable livelihood options to reduce human-wildlife conflicts.
The study by Nampindo and Randhir offers a critical roadmap for the conservation of African elephants in the Greater Virunga Landscape. By focusing on the dynamic interplay between climate change, habitat loss, and elephant population dynamics, their work provides valuable insights for crafting resilient conservation strategies. As we face the challenges of a changing planet, such research is indispensable for guiding our efforts to preserve the natural world and its magnificent inhabitants.
Final Thoughts
This comprehensive study not only advances our understanding of the intricate relationships between elephants and their environment but also serves as a clarion call for urgent, collaborative conservation action. The fate of Africa’s elephants hangs in the balance, and it is incumbent upon us all to heed this call and act decisively to secure their future.

